FOCUS: Male Infertitlity
Did you know that 7.5% of all sexually experienced men younger than age 45 reported seeing a fertility doctor during their lifetime?
FOCUS: Female Infertitlity
Did you know that 6-10% of married women 15–44 years of age are unable to get pregnant after one year of unprotected sex ?
OVARIAN CYSTS
-
What are ovaries?
The ovaries (OH-vuh-reez) are a pair of organs in the female reproductive system. They are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. The uterus (YOO-tur-uhss) is the hollow, pear-shaped organ where a baby grows. Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond. The ovaries produce eggs and female hormones. Hormones are chemicals that control the way certain cells or organs function.
Every month, during a woman's menstrual (MEN-stroo-uhl) cycle, an egg grows inside an ovary. It grows in a tiny sac called a follicle (FAH-lih-cull). When an egg matures, the sac breaks open to release the egg. The egg travels through the fallopian (fuh-LOH-pee-ihn) tube to the uterus for fertilization. Then the sac dissolves. The empty sac becomes corpus luteum (LOO-tee-uhm). Corpus luteum makes hormones that help prepare for the next egg.
The ovaries are the main source of the female hormones estrogen (ESS-truh-juhn) and progesterone (proh-JESS-tuh-rohn). These hormones affect:
- the way breasts and body hair grow
- body shape
- the menstrual cycle
- pregnancy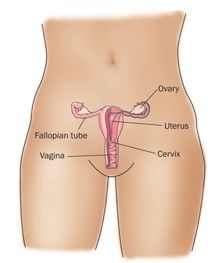
-
What are ovarian cysts?
A cyst is a fluid-filled sac. They can form anywhere in the body. Ovarian cysts (sists) form in or on the ovaries. The most common type of ovarian cyst is a functional cyst.
Functional cysts often form during the menstrual cycle. The two types are:
- Follicle cysts These cysts form when the sac doesn't break open to release the egg. Then the sac keeps growing. This type of cyst most often goes away in 1 to 3 months.
- Corpus luteum cysts These cysts form if the sac doesn't dissolve. Instead, the sac seals off after the egg is released. Then fluid builds up inside. Most of these cysts go away after a few weeks. They can grow to almost 4 inches. They may bleed or twist the ovary and cause pain. They are rarely cancerous. Some drugs used to cause ovulation, such as Clomid® or Serophene®, can raise the risk of getting these cysts.
Other types of ovarian cysts are:
- Endometriomas (EN-doh-MEE-tree-OH-muhs) These cysts form in women who have endometriosis (EN-doh-MEE-tree-OH-suhss). This problem occurs when tissue that looks and acts like the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. The tissue may attach to the ovary and form a growth. These cysts can be painful during sex and during your period.
- Cystadenomas (siss-tahd-uh-NOH-muhs) These cysts form from cells on the outer surface of the ovary. They are often filled with a watery fluid or thick, sticky gel. They can become large and cause pain.
- Dermoid (DUR-moid) cysts These cysts contain many types of cells. They may be filled with hair, teeth, and other tissues that become part of the cyst. They can become large and cause pain.
- Polycystic (pol-ee-SISS-tik) ovaries These cysts are caused when eggs mature within the sacs but are not released. The cycle then repeats. The sacs continue to grow and many cysts form. For more information about polycystic ovaries, refer to our FAQ about Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. -
What are the symptoms of ovarian cysts?
Many ovarian cysts don't cause symptoms. Others can cause:
- pressure, swelling, or pain in the abdomen
pelvic pain
- dull ache in the lower back and thighs
- problems passing urine completely
- pain during sex
- weight gain
- pain during your period
- abnormal bleeding
- nausea or vomiting
- breast tenderness
If you have these symptoms, get help right away:
- pain with fever and vomiting
- sudden, severe abdominal pain
- faintness, dizziness, or weakness
- rapid breathing -
How are ovarian cysts found?
Doctors most often find ovarian cysts during routine pelvic exams. The doctor may feel the swelling of a cyst on the ovary. Once a cyst is found, tests are done to help plan treatment. Tests include:
- An ultrasound This test uses sound waves to create images of the body. With an ultrasound, the doctor can see the cyst's:
- shape
- size
- location
- mass—if it is fluid-filled, solid, or mixed
- A pregnancy test This test may be given to rule out pregnancy.
- Hormone level tests Hormone levels may be checked to see if there are hormone-related problems.
A blood test This test is done to find out if the cyst may be cancerous. The test measures a substance in the blood called cancer-antigen 125 (CA-125). The amount of CA-125 is higher with ovarian cancer. But some ovarian cancers don't make enough CA-125 to be detected by the test. Some noncancerous diseases also raise CA-125 levels. Those diseases include uterine fibroids (YOO-tur-ihn FEYE-broidz) and endometriosis. Noncancerous causes of higher CA-125 are more common in women younger than 35. Ovarian cancer is very rare in this age group. The CA-125 test is most often given to women who:
- are older than 35
- are at high risk for ovarian cancer
- have a cyst that is partly solid -
How are cysts treated?
Watchful waiting : If you have a cyst, you may be told to wait and have a second exam in 1 to 3 months. Your doctor will check to see if the cyst has changed in size. This is a common treatment option for women who:
- are in their childbearing years
- have no symptoms
- have a fluid-filled cyst
It may be an option for postmenopausal women.
Surgery : Your doctor may want to remove the cyst if you are postmenopausal or if it:
- doesn't go away after several menstrual cycles
- gets larger
- looks odd on the ultrasound
- causes pain
The two main surgeries are:
- Laparoscopy (lap-uh-ROSS-kuh-pee)—done if the cyst is small and looks benign (noncancerous) on the ultrasound. While you are under general anesthesia, a very small cut is made above or below your navel. A small instrument that acts like a telescope is put into your abdomen. Then your doctor can remove the cyst.
- Laparotomy (lap-uh-ROT-uh-mee)—done if the cyst is large and may be cancerous. While you are under general anesthesia, larger incisions are made in the stomach to remove the cyst. The cyst is then tested for cancer. If it is cancerous, the doctor may need to take out the ovary and other tissues, like the uterus. If only one ovary is taken out, your body is still fertile and can still produce estrogen.
Birth control pills : If you keep forming functional cysts, your doctor may prescribe birth control pills to stop you from ovulating. If you don’t ovulate, you are less likely to form new cysts. You can also use Depo-Provera®. It is a hormone that is injected into muscle. It prevents ovulation for 3 months at a time. -
Can ovarian cysts be prevented?
No, ovarian cysts cannot be prevented. The good news is that most cysts:
- don't cause symptoms
- are not cancerous
- go away on their own
Talk to your doctor or nurse if you notice:
- changes in your period
- pain in the pelvic area
- any of the major symptoms of cysts -
When are women most likely to have ovarian cysts?
Most functional ovarian cysts occur during childbearing years. And most of those cysts are not cancerous. Women who are past menopause (ages 50–70) with ovarian cysts have a higher risk of ovarian cancer. At any age, if you think you have a cyst, see your doctor for a pelvic exam.
LOVE QUOTE OF THE DAY
"Love you will find only where you may show yourself weak without provoking strength."
